How To Calculate MOQ?
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) plays a crucial role in inventory management, helping businesses maintain cost efficiency while ensuring a steady supply. It represents the smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell or a business needs to order to make a purchase economically viable.
Determining the optimal MOQ is essential for balancing supply chain efficiency, cost control, and storage capacity. By calculating MOQ effectively, businesses can reduce waste, negotiate better supplier terms, and prevent excess inventory issues.
What is Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)?

Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier requires a buyer to purchase in a single order. Suppliers set MOQ to ensure cost efficiency in production, packaging, and distribution. Businesses must consider MOQ when managing inventory, as it impacts purchasing costs, stock levels, and supplier negotiations. Finding the right balance helps businesses optimize expenses while maintaining a steady supply of goods.
Importance of Understanding MOQ
MOQ impacts cost management, inventory efficiency, and cash flow, helping businesses balance savings and operational needs. It reduces costs by avoiding frequent small orders and leveraging bulk purchases. A well-calculated MOQ streamlines procurement, storage, and supplier negotiations.
By managing MOQ strategically, businesses prevent stock issues, improve supply chain efficiency, and allocate resources effectively for growth and stability.
How to Calculate Minimum Order Quantity?
Calculating Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) involves several key steps to ensure businesses optimize their purchasing decisions while minimizing costs and inventory risks.
Step 1: Gathering Information
The first step in calculating Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) is gathering essential data to ensure an accurate and cost-effective order size. Businesses need to identify key variables that influence purchasing decisions, including:
- Demand Forecast: Estimating how much product is needed over a specific period to avoid overstocking or shortages.
- Storage Costs: Understanding warehousing expenses, including rent, handling, and insurance, to ensure efficient inventory levels.
- Supplier Constraints: Reviewing supplier-imposed MOQs, pricing tiers, and bulk discount opportunities that impact purchasing flexibility.
Step 2: Understanding Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
EOQ helps businesses determine the optimal order size to minimize costs, influencing Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) decisions. It balances ordering costs and holding costs to ensure efficient inventory management.
EOQ Formula:

Where:
D = Annual demand
S = Ordering cost per order
H = Holding cost per unit per year
Step 3: Considering Constraints and Practicality
Before finalizing the Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ), businesses must account for practical constraints to ensure efficient inventory management.
- Supplier Restrictions: Many suppliers enforce MOQ policies, requiring buyers to purchase a set minimum quantity per order.
- Bulk Discounts: Suppliers often offer lower prices for larger orders, influencing the decision to adjust the MOQ for cost savings.
- Storage Capacity: Businesses need to assess their warehouse space and holding costs to avoid excess inventory that strains resources.
Step 4: Adjusting EOQ for Constraints
Once the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is calculated, businesses must refine it based on real-world limitations to ensure practical application.
- Supplier Requirements: If EOQ is lower than the supplier’s MOQ, adjustments must be made to meet purchasing conditions.
- Budget Constraints: Businesses should evaluate financial feasibility to avoid excessive spending on bulk orders.
- Storage Limitations: Warehousing space must align with the ordered quantity to prevent inefficiencies.
Step 5: Calculation of Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
Once key factors like demand, costs, and supplier requirements are identified, businesses can calculate MOQ using a structured approach.
- Assess Demand: Determine the expected sales volume over a given period.
- Factor in Ordering & Holding Costs: Balance bulk ordering costs with storage expenses to optimize purchasing efficiency.
- Review Supplier MOQ: Align calculations with supplier-imposed minimum order limits.
- Apply Adjusted EOQ: Modify the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) formula based on constraints to find the most practical MOQ.
Step 6: Review and Iteration
Once the Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) is calculated, businesses should periodically refine it to align with market trends and operational needs.
- Adjust for Demand Fluctuations: If sales patterns change, update MOQ to prevent overstocking or shortages.
- Monitor Supplier Terms: Suppliers may modify their MOQ policies, requiring adjustments in purchasing strategy.
- Reevaluate Cost Factors: Changes in ordering, storage, or bulk pricing should be considered when revising the MOQ.
- Analyze Business Growth: Expanding operations may call for a higher MOQ to meet increased customer demand efficiently.
Step 7: Documentation and Communication
Recording Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) decisions ensures clear supplier negotiations and effective inventory planning.
- Keep detailed records: Document demand, cost factors, and supplier constraints.
- Communicate with suppliers: Align MOQ with purchasing agreements and supply needs.
- Integrate into inventory systems: Use digital tools for automated tracking and order planning.
What Types of MOQs Exist?
MOQ varies based on business and supplier requirements. The 3 common types are:
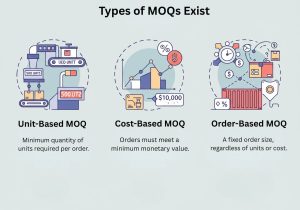
- Unit-Based MOQ: Minimum quantity of units required per order.
- Cost-Based MOQ: Orders must meet a minimum monetary value.
- Order-Based MOQ: A fixed order size, regardless of units or cost.
How Do MOQs Impact Inventory Management?
MOQ affects inventory by influencing stock levels, procurement efficiency, and business operations.
- Stock Levels: High MOQ may lead to excess inventory, while low MOQ offers flexibility but risks shortages.
- Procurement Efficiency: Proper MOQ planning reduces reordering costs and optimizes supplier negotiations.
- Business Operations: Balanced MOQ improves cash flow, minimizes storage expenses, and ensures smooth inventory flow.
What Are the Benefits of MOQs?
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) offers several advantages, particularly in cost management and supply chain optimization.
Cost Saving
- Bulk purchasing lowers the per-unit cost, increasing overall profitability.
- Reduces ordering frequency, cutting administrative and logistical expenses.
- Helps businesses negotiate better pricing with suppliers.
Supply Chain Efficiency
- Strengthens supplier relationships by ensuring consistent order volumes.
- Streamlines procurement, reducing delays and improving inventory planning.
- Prevents frequent stock shortages, ensuring smooth business operations.
Conclusion
Determining Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) ensures cost-efficient procurement, supplier negotiations, and smooth operations. A strong MOQ strategy reduces expenses, minimizes holding costs, and prevents stock issues, improving cash flow. Businesses should regularly refine MOQ calculations to adapt to market changes, ensuring long-term efficiency and profitability.
If you liked this article, don’t forget to subscribe to our newsletter to get more exciting articles, news, and offers right in your inbox. Also, follow us on Facebook, Instagram, and Dribble to stay updated.
FAQ’s on How to Calculate MOQ
1. What is MOQ, and why is it important?
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) is the smallest amount a supplier requires a buyer to purchase in one order. It helps businesses optimize costs, manage inventory efficiently, and ensure stable supplier relationships.
2. How do I determine the right MOQ for my business?
Start by analyzing demand forecasts, ordering costs, storage capacity, and supplier constraints. Using Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) as a guideline can help refine MOQ for cost-effectiveness.
3. What is the formula for calculating MOQ?
There is no universal formula, but MOQ is often determined by adjusting EOQ, factoring in supplier requirements, financial constraints, and storage limitations.
The EOQ formula is:

Where D = Demand, S = Ordering cost, and H = Holding cost.
4. How do supplier-imposed MOQs affect my purchasing strategy?
Suppliers set MOQs based on their production costs. If a supplier’s MOQ is higher than your calculated EOQ, you may need to negotiate terms or collaborate with other buyers to meet the MOQ.
5. What are the risks of setting an MOQ too high or too low?
- High MOQ – Leads to excessive inventory, increased storage costs, and cash flow constraints.
- Low MOQ – May result in higher per-unit costs, frequent reordering, and inefficient procurement.
6. Can MOQ change over time?
Yes, businesses should regularly review and adjust MOQ based on demand fluctuations, supplier terms, and market conditions to ensure cost-effective inventory management.
7. How can I negotiate the MOQ with suppliers?
Discuss order flexibility, bulk discounts, and long-term purchasing agreements. Showing consistent demand may help lower MOQ requirements.

